Cryptojacking:
Definition, Detection
& Prevention Tips
What is cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a digital money that operates as a medium of exchange. People earn cryptocurrency by using computers either to solve or verify the solutions of maths problems called hashes. There are hundreds of types of cryptocurrencies, and each has its own coin or token. Each cryptocurrency that was invented has its use case to solve any existing problems.
The world’s biggest and most well-known cryptocurrency, Bitcoin surged in 2021 to reach its all-time high of $69,000 in November 2021. It also has pulled up the value of other popular cryptocurrencies like Ethereum ($ETH), Binance Coin ($BNB), Ripple ($XRP), and Monero ($XMR).

Top cryptocurrencies in the market.
The advantage of this kind of currency is its digital payment system that does not rely on banks to verify transactions. Governments and regulators do not have figured out appropriate business norms and legal structure for managing and governing it. This is where cybercriminals can benefit.
What is cryptojacking?
Cryptojacking is a type of cybercrime where a hacker co-opts a target’s computing power to secretly mine cryptocurrency on the hacker’s behalf. Instead of building and expending dedicated crypto mining rigs, hackers use cryptojacking to steal computing resources from their victim’s devices.
Cryptojacking can be targeted at individual consumers, massive institutions, and even industrial control systems. It is a scheme to use people’s devices such as computers, smartphones, tablets or servers. Hackers are able to compete against sophisticated crypto mining operations without the costly overhead.
How does cryptojacking work?
Hackers have more than one way to enslave victims’ computers. Cryptojacking assaults seize its victim using three methods: file-based, browser-based, and cloud cryptojacking. Each strategy has different techniques and courses of action that give an impact on the target.
-
File-based Cryptojacking
 It involves downloading and executing malware files. The malware features an infected script that spreads its impact throughout the targeted infrastructure upon successfully executing.
It involves downloading and executing malware files. The malware features an infected script that spreads its impact throughout the targeted infrastructure upon successfully executing.
One of the common methods is using email to spread such malicious files and links. The email is made up as a legitimate email written in a proper format. Victims are lured to download or open the file. As soon as the steps are done, the script becomes active and starts working stealthily without the user’s knowledge.
-
Browser-based Cryptojacking
 The method begins with hackers generating maliciously programmed scripts for cryptojacking. The next step is it is embedded directly in numerous web pages of separate sites. The script is run automatically and when a user visits the infected URL, their devices will download the code and support hackers in cryptojacking tasks unintentionally.
The method begins with hackers generating maliciously programmed scripts for cryptojacking. The next step is it is embedded directly in numerous web pages of separate sites. The script is run automatically and when a user visits the infected URL, their devices will download the code and support hackers in cryptojacking tasks unintentionally.
The hackers can hide malicious scripts by embedding them in ads and outdated plugins. Some attacks can be smarter, as the script compromises the JavaScript library. It can be used to perform a bigger supply chain attack on the victim’s IT environment.
-
Cloud Cryptojacking
 Hackers use the method to get access to the victim’s essential resources at a large scale. They will search through an organisation’s files and code for API keys to access the target cloud services.
Hackers use the method to get access to the victim’s essential resources at a large scale. They will search through an organisation’s files and code for API keys to access the target cloud services.
Therefore, hackers are able to consume the CPU resources without any limitations. It enables mining to a big level and faster to illicitly mine for currency. The impact results where the victim might be charged with a huge amount on their cloud services account.
How to detect cryptojacking?
-
Reduce Performance
The most significant symptom of cryptojacking is decreased performance on computing devices. Using computers to mine cryptocurrencies requires a lot of energy and process power. When Central Processing Unit (CPU) usage is high, the computer is struggling to perform other tasks. Victims might experience slow processing, unexpected shutdown, and failures in opening certain apps and software. Another indicator is the device’s battery drains more quickly than it usually does.
-
Excessive Heating
The extra resource consumption of cryptojacking leads to device overburden and makes it overheat. Overheating may shorten the average lifespan of the devices and might increase the cost to replace new devices. Moreover, computer fans might run longer than they should in order to cool down the device.
-
Monitor the CPU Usage
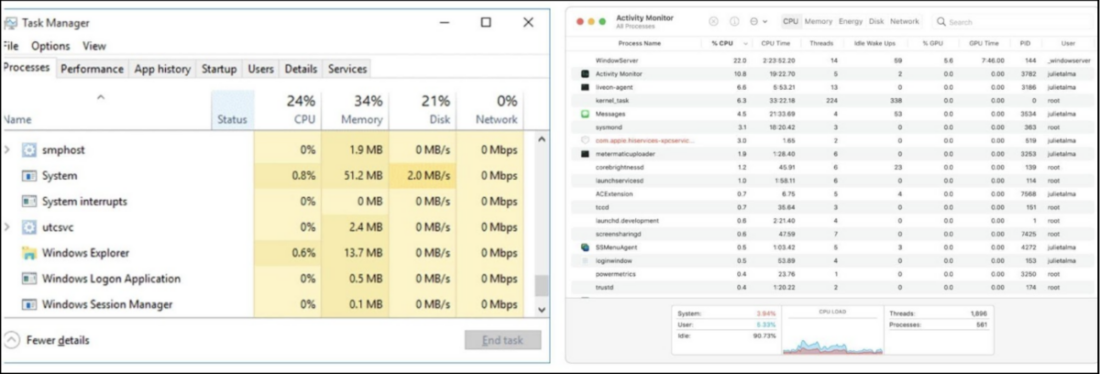
If users see an increase in CPU usage when users are on a website with little or no media content, it could be a sign of Cryptojacking running in the background. A good cryptojacking test is to check the CPU usage through Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (macOS). However, some cryptojacking processes might be hiding or masking something that looks legitimate.
How to stop cryptojacking?
-
Use an Anti-crypto Mining Browser Extension
Cryptojacking scripts are often deployed in web browsers. Some browser extensions such as No Coin, minerBlock, and Anti Minder can be installed in Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox. The user’s web browser also must be up-to-date in order to equip with basic defences against recent cryptojacking attacks.
-
Use Ad-blockers
Since Cryptojacking scripts are often delivered through online ads, users must be protected by using an ad-blocker. This program can effectively detect and block malicious cryptojacking scripts and stop them from being loaded.
-
Disable JavaScript
JavaScript can be disabled to prevent cryptojacking when browsing online. However, some of the functions that users require might be blocked to protect them from being drive-by cryptojacking.
-
Use Endpoint Protection
There are endpoint protections/antivirus that have added crypto miner detection to their product. ArmourZero partnering with DNSFilter provides total web protection and has the best range of prices to block cryptohackers from stealing computer’s power and resources to mine digital coins.

Written by:
Muhammad Syafiq bin Abas, experienced in Technical Support Engineer (System Security) in the information technology and services industry.
Share this post
Related Posts

Earth Day: The Connection of Cybersecurity and Sustainability
- 22 Apr 2024
- By:Fanny Fajarianti
- Category: ArmourHacks
Uncover the link between Earth Day and Cybersecurity, promoting sustainability through data protection and environmental stewardship. Let’s secure a greener future.

What is DevSecOps? Definition & Best Practices for Tech Industries
- 18 Apr 2024
- By:Bernadetta Septarini
- Category: ArmourHacks
Learn about DevSecOps, principles, and best practices for the tech industry. Integrate security seamlessly into software development and enhance quality.

Safeguarding Your Organisation During the Hari Raya Holiday
- 09 Apr 2024
- By:Bernadetta Septarini
- Category: ArmourHacks
Protect your organisation from holiday cyberattacks during Hari Raya. Learn more about the risks and best practices for holiday security with ArmourZero.

Cyberattacks: A Growing Threat to Higher Education
- 02 Apr 2024
- By:Fanny Fajarianti
- Category: ArmourHacks
Universities hold sensitive data but face cyberattack risks in the digital age. Explore the impact of cyberattack and learn how to protect your institution.


